Leetcode算法之二叉树
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树。
注意:
你可以假设树中没有重复的元素。
例如,给出
前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
1 | |
思路:
(1)前序遍历:根节点->左节点->右节点;中序遍历:左子树->根节点->右子树
(2)利用前序遍历中的根节点将中序遍历数组拆分成俩部分,分别为当前根节点的左子树和右子树
(3)递归解决每个根节点的左子树和右子树问题
1 | |
662. 二叉树最大宽度
给定一个二叉树,编写一个函数来获取这个树的最大宽度。树的宽度是所有层中的最大宽度。这个二叉树与满二叉树(full binary tree)结构相同,但一些节点为空。
每一层的宽度被定义为两个端点(该层最左和最右的非空节点,两端点间的null节点也计入长度)之间的长度。
1 | |
思路:
- 求最大宽度,那么如果我们能求到最靠近左边的节点,保存下标;然后求得最后边的节点,利用下标之差,注意这个节点的父亲节点的父亲节点可能存在左子树。
- 题目有提到说类似于满二叉树结构,所以如果根节点下标设为i(i>=1),那么根节点的左节点2 *i,右节点2 *i+1;
- 使用一个map来存放每一层最左边的节点的下标
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47class Solution {
public:
unsigned long long maxwidth = 0;
map<int, unsigned long long> mp;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int level, unsigned long long index)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
if(!mp.count(level))
mp[level] = index;
maxwidth = max(maxwidth, index - mp[level] + 1);
dfs(root->left, level+1, index*2+1);
dfs(root->right, level+1, index*2+2);
}
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root, 0, 0);
return maxwidth;
}
};// 非递归
class Solution {
public:
int maxwidth = 0;
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL)
return maxwidth;
queue<pair<TreeNode*, int>> qt;
vector<int> start;
qt.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(root, 1));
while(!qt.empty())
{
pair<TreeNode*, int> p = qt.front();
start.push_back(p.second);
for(int i = 0; i < qt.size(); ++i)
{
pair<TreeNode*, int> tp = qt.front();
qt.pop();
maxwidth = max(maxwidth, tp.second - p.second + 1);
if(tp.first->left)
qt.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(tp.first->left, 2*tp.second));
if(tp.first->right)
qt.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(tp.first->left, 2*tp.second+1));
}
}
return maxwidth;
}
};
543. 二叉树的直径
给定一棵二叉树,你需要计算它的直径长度。一棵二叉树的直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值。这条路径可能穿过也可能不穿过根结点。
1 | |
返回 3, 它的长度是路径 [4,2,1,3] 或者 [5,2,1,3]。
注意:两结点之间的路径长度是以它们之间边的数目表示。
思路:
- 直径的概念:俩个节点之间的路径长度,对于每一个节点来说,就是左子树长度+右子树长度
- 求最大直径,比较所有节点的直径,取最大值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17class Solution {
int ans;
int diameter(TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int l = diameter(root->left);
int r = diameter(root->right);
ans = max(ans, l + r);
return max(l,r) + 1;
}
public:
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
ans = 0;
diameter(root);
return ans;
}
};
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
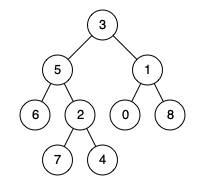](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200908085313373.png#pic_center)
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出: 3
解释: 节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3。
输入: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
输出: 5
解释: 节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
所有节点的值都是唯一的。
p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉树中。
思路:
分析二叉树的结构,左子树,右子树, 根节点,给定俩个节点,找最近公共祖先
(1)当某一节点A在另一节B点的左子树或右子树中,则B为最近公共祖先,反之亦然
(2)如果一个节点C的左子树和右子树分别包含A,B节点,则C为AB的公共祖先,那么如何保证C为最近公共祖先呢?当我们采用递归的方式查找(递归到叶子节点回退判断)的时候,最先查找的节点就是最近的点,直接返回即可。
1 | |
257. 二叉树的所有路径
给定一个二叉树,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
1 | |
思路:
- 回溯的方法
- 使用vector
先存储,存完后转string 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34class Solution {
public:
vector<string> path;
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> vc;
TreePath(root,vc);
return path;
}
void TreePath(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& vc)
{
if(root == NULL)
return;
vc.push_back(root->val);
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
string str = "";
for(int i = 0; i < vc.size(); ++i)
{
cout << vc[i];
str += to_string(vc[i]);
if(i != vc.size()-1)
str += "->";
}
cout << endl;
path.push_back(str);
vc.pop_back();
return;
}
TreePath(root->left, vc);
TreePath(root->right, vc);
vc.pop_back();
}
};